Combined Cycles
Warning: Undefined variable $scroller in /var/general-sites/radmaxtech.com/www/view/template/main/body.php on line 10
Warning: Undefined variable $booth in /var/general-sites/radmaxtech.com/www/view/template/main/body.php on line 11
RadMax® Combined Cycles
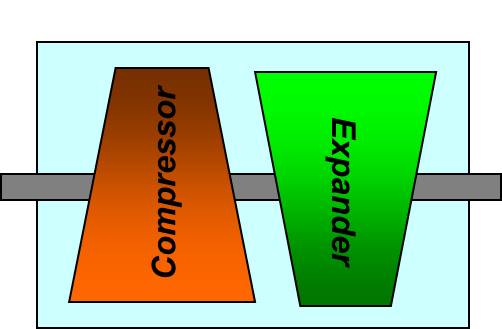
A RadMax technology device is comprised of two cams connected by a common driveshaft in a single housing. By using separate vane actuator systems, each cam can have a different compression or expansion ratio, making it possible to have two separately functioning cam cycles (i.e., engine, pump, compressor, gas expander) in the same device. The resulting compact device provides flexible functionality and high performance in a small footprint.
Examples of a combined-cycle device include:
Internal-combustion engine on one side driving a compressor or pump on the other side
Gas expander on one side driving a compressor or pump on the other side
A RadMax combined-cycle device is characterized by:
- Increased design flexibility and functionality
- Compact size with high performance
- Reduced size, weight, parts count and cost
- Reduced complexity
- Rapid field change-out capability
- Capability to utilize and combine Brayton, Rankine and Organic Rankine cycles to best suit the requirements of the application
- Scalable from small to very large devices
RadMax Combined Cycle
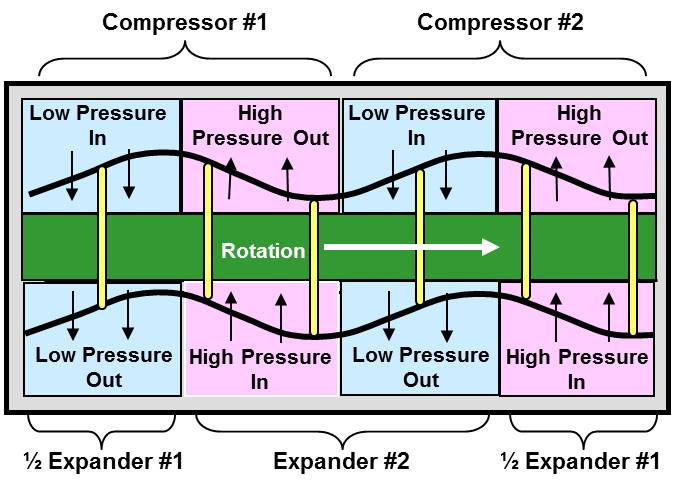
The RadMax two-cam design allows for differently configured cams to operate independently on each side of the device, a combination of four distinct sections with two complete intake and discharge cycles on each cam. This unique design allows for each of these sections to be configured with different compression, expansion, or pump ratios. Different porting options into and between the sections allow for multi-stage expansion in one device. Additionally, the device has the potential to integrate an electric generator within the unit, creating a compact genset.
RadMax Combined-Cycle Device Operation
In a RadMax device, the vanes move axially driven by the rotor face. The pressure in each chamber changes when the adjacent vanes extend or retract. During rotor revolution, the ends of the vanes follow a path that approximates a sinusoidal wave. This path is uniquely designed so that during each revolution of the rotor, the chambers’ volumes alternately expand and contract.
The process is repeated in each of the sections, in each chamber, and on each side of the rotor. The rotor spins continuously in one direction rather than violently changing directions as with pistons in a reciprocating device. Because the upper and lower faces of the rotor are 90-degrees out of phase, the RadMax gas expander is always balanced and exhibits minimal vibration.
Applications
Due to their compact size, high power-to-weight ratio and high efficiency, RadMax combined-cycle devices are well suited for applications with weight restrictions and limited space, such as auxiliary and backup power generation, waste heat recovery, portable pumps, compressors and generators, and gas system throttling loss recovery.